2.3 Assignment and Analysis When judging the relative importance of elements in a hierarchy, qualitative and quantitative analysis methods are used, which include both the scores given by experts based on their knowledge and experience, and the scores determined based on numerical comparisons. Constructing various types of judgment matrices from these two types of scores. When analyzing the research object(s), it included nine impact factors (M) such as investment amount, operation fee, energy consumption, pass rate, acidification, global warming, waste treatment, noise, and sensitive points. A total of three indicators (p) are provided at the highest level of comprehensive benefits: economic benefits, technical performance, and environmental benefits. If the problem of environmental benefits is highlighted in the survey, then the scale value should be assigned the highest of the three, and the construction judgment matrix is ​​as follows:
Judgment matrix A-P
The normalization of each column of the judgment matrix is ​​as follows:
┌0.111 0.077 0.130â”
│0.333 0.231 0.217│
└ 0.556 0.692 0.652 ┘
The resulting vector 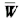 =[0.318,0.781,1.900]T, normalize it, then find the eigenvector W=[0.106,0.261,0.634]T.
=[0.318,0.781,1.900]T, normalize it, then find the eigenvector W=[0.106,0.261,0.634]T.
Calculate the maximum eigenvalue λmax of the judgment matrix:
From this, the maximum eigenvalue of the AP matrix is ​​λmax = 3.036, and the corresponding eigenvector W = [0.106, 0.261, 0.6347]T, where the three components are the weights of the three elements P1, P2, and P3 in the criterion layer P. value. Consistency check CR=CI/RI0.035<0.1, that is, the weights in W can be applied. Then the judgment matrix Pn-M and Mn-S are constructed, and the maximum eigenvalue and eigenvector are also calculated, and the consistency check is performed.
Through the above operations, hierarchical single-level sorting, hierarchical one-level total sorting, and hierarchical two-level total sorting are completed. The hierarchical total ranking results are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Level 2 total sort
From the results of the total ranking of levels, we can see that under the premise of focusing on environmental benefits as the focus of inspection objectives, the three factors of comprehensive economic benefits, technical performance and environmental benefits, the weight value obtained by the first paper mold factory is 0.580, and the second paper The weight of the mold factory is 0.420, which means that the first paper mold factory is better than the second paper mold factory. Similarly, on the premise of focusing on economic benefits as the focus of the inspection objectives, the total ranking of the levels is performed. The results show that the weight value obtained by the first paper mold factory is 0.6, and the weight obtained by the second paper mold factory is 0.4. Under the premise of focusing on the technical performance as the focus of inspection objectives, the total ranking of the levels is performed. The results show that the weight value obtained by the first paper mold factory is 0.54, and the weight obtained by the second paper mold factory is 0.46.
In summary, the first paper-molding plant is better than the second paper in terms of the environmental benefits most concerned by environmental managers or the economic benefits most concerned by the company's managers or the technical performance of the product users. Mold factory. Especially in terms of economic benefits and environmental benefits, the advantages of the first paper molding factory are even more obvious. Therefore, the first paper molding product factory is the first choice for building a new factory or an old factory.
3 Conclusion
Based on the LCA theory, the data collection and evaluation are started from the perspective of environmental issues. At the same time, economic and technical performance factors are taken into consideration. The comprehensive evaluation model is constructed using the analytic hierarchy process to make the package product production system with multi-factor characteristics more practical.
Discussion on Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Packaging Products Department of Printing and Packaging Engineering, Dalian Liberal Institute of Light Industry, Huo Lijiang, Dalian, Liaoning 116034, China
[Abstract] According to the theory of life cycle assessment, comprehensive evaluation of packaging products is conducted to explore the effective mode of ecological packaging manufacturing.
Key words: life cycle assessment; paper mold; AHP Based on LCA theory, a comprehensive analysis of the production process of packaging products is conducted to determine the production system that is more in line with the green packaging engineering requirements. According to the definition of objectives, the research focused on the production of 25-inch color television paper mold packaging as a functional unit, focusing on the differences in the environmental impact, economic benefits, and technical performance of two different paper mold packaging product manufacturing systems. Therefore, when the scope is defined, the acquisition of raw materials is used as the beginning of this life cycle evaluation study to obtain the finished product of paper mold packaging products as the end of this life cycle evaluation study.
1 Inventory analysis The survey production statistics, material balance, and key workshop water, electricity, and oil consumption were calculated. The factors such as personnel salaries, depreciation of fixed assets, and period expenses were taken into consideration. The data list is shown in Table 1. Product qualification rate
Fruit Tools,Lemon Squeezer,Lemon Juice Squeezer,Pineapple Corer
Xiongyang Household Co., Ltd , https://www.nbyjkitchen-manage.com
